LED (Light Emitting Diode)
LED is an abbreviation for Light Emitting Diode. Electrical energy is transferred to optical energy in semiconductor crystal. ; The most common function of a diode is to allow electric current to pass in one direction.
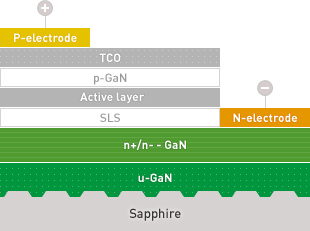
The LED structure consists of a p-GaN, n-GaN and multi-quantum well (MQW) layers which contain electrons and holes which recombine to emit the light.
The wavelength of the emitting light depends on the band-gap of MQW. The band gap is controlled by the alloy composition of the MQW.
Advantages of LEDs
- High electrical efficiency
- Long life time : more than 50,000 HR
- High durability and small size comparing to conventional light sources.
- Eco-friendly and low cost
- Fast on/off time
Ways to build white LEDs
White LED’s performance, usually, is measured by these factors ; Efficiency, Similarity to natural light, Color rendition, Color index realization. Ways to produce white LED is as below.
The way to make White LED
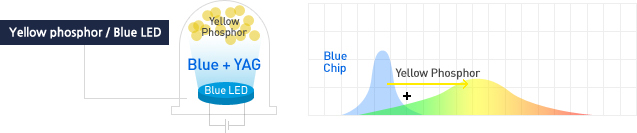
[Blue LED + Yellow phosphor]
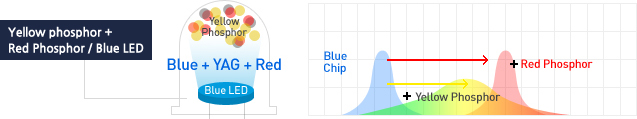
[Blue LED + Yellow, red phosphor]
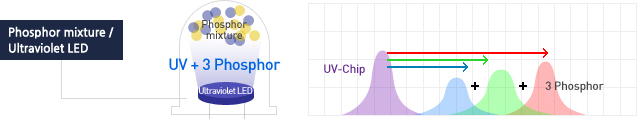
[UV LED + Blue, green, red phosphor]
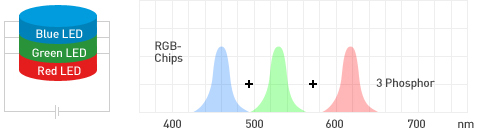
[Combination of Blue, green, red LEDs]
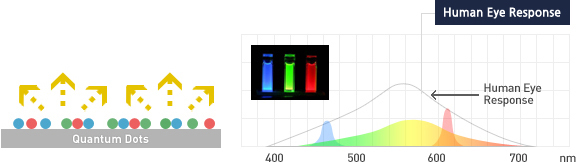
[Blue LED + Quatum dot phosphor]